Advanced Search
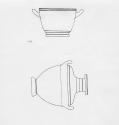
Drinking cup (skyphos) with the departure and recovery of Helen
Greek
Late Archaic Period
about 490 B.C.
Place of Manufacture: Greece, Attica, Athens
Medium/Technique
Ceramic, Red Figure
Dimensions
Height: 21.5 cm (8 7/16 in.); diameter: 39 cm (15 3/8 in.); diameter of mouth: 27.8 cm (10 15/16 in.)
Credit Line
Bartlett Collection—Museum purchase with funds from the Francis Bartlett Donation of 1912
Accession Number13.186
NOT ON VIEW
CollectionsAncient Greece and Rome
ClassificationsVessels
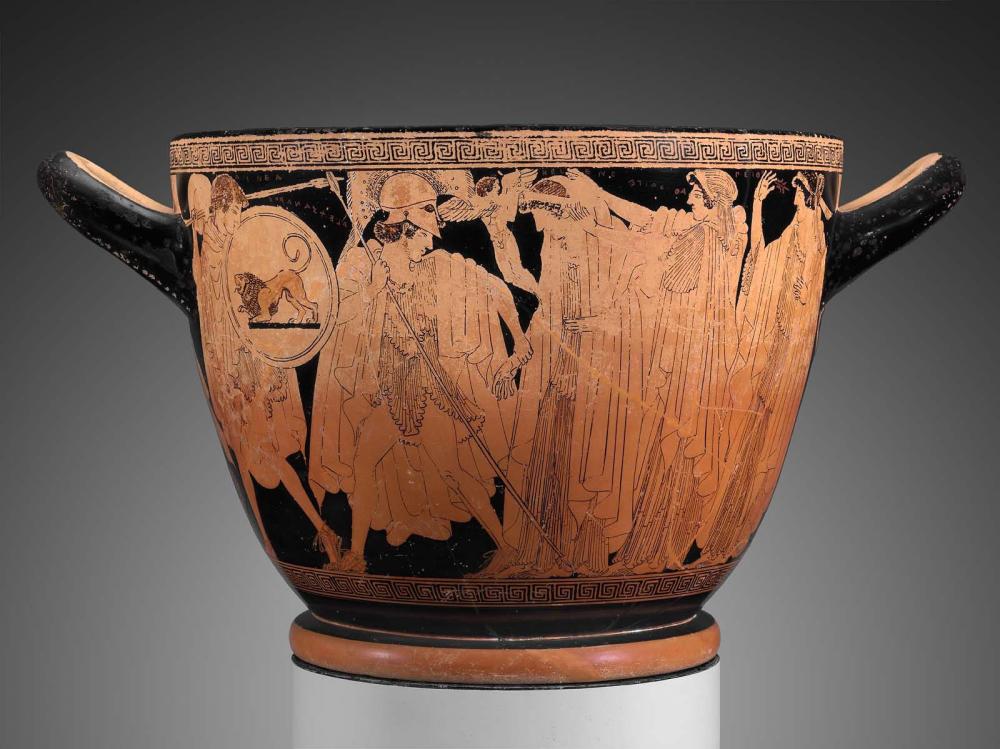
Visual vignettes of the beginning and end of the Trojan War decorate this skyphos, a form of drinking cup. An initial scene shows Paris (identified by his alternate name, Alexandros) arriving at Sparta to claim Helen as his bride. Helen was reluctant to leave her home, husband, and son (probably the small boy beneath one handle), until Aphrodite filled her with love-embodied by the tiny winged Eros close to her face-for Paris. Combining forces, Aphrodite veils Helen while Peitho (Persuasion) waves her on. Paris grasps Helen's hand, a gesture signifying both abduction and marriage, two concepts often conflated in the ancient world. This act began the war: Helen's husband Menelaos called on other Greeks, notably his powerful brother Agamemnon, to help him recover his wife.
In the concluding scene, set in Troy during the fall of the city, a vengeful Menelaos finds Helen in the Sanctuary of Apollo. Once again, Aphrodite comes to Helen's aid, this time removing her veil so that Menelaos, overcome by her beauty, will drop his sword. The priest of the sanctuary, Chryses, and his daughter, Chryseis, witness the action, as does Priam, the king of Troy, who is seated under the handle at the right. These supporting characters flesh out additional details of the conflict: Priam, too old to fight, watched many of the battles from the city's walls, and Chryses and Chryseis figure prominently in the first book of Homer's Iliad, bringing both plague and internal conflict to the Greek forces.
The artist responsible for this beautiful and complex rendering of the framing episodes of the Trojan conflict was Makron, one of the most influential red-figure painters in early fifth-century-B.C. Athens. He was exceptionally prolific, with more than six hundred extant vases attributed to him, and he appears to have worked exclusively with one potter, Hieron.
In the concluding scene, set in Troy during the fall of the city, a vengeful Menelaos finds Helen in the Sanctuary of Apollo. Once again, Aphrodite comes to Helen's aid, this time removing her veil so that Menelaos, overcome by her beauty, will drop his sword. The priest of the sanctuary, Chryses, and his daughter, Chryseis, witness the action, as does Priam, the king of Troy, who is seated under the handle at the right. These supporting characters flesh out additional details of the conflict: Priam, too old to fight, watched many of the battles from the city's walls, and Chryses and Chryseis figure prominently in the first book of Homer's Iliad, bringing both plague and internal conflict to the Greek forces.
The artist responsible for this beautiful and complex rendering of the framing episodes of the Trojan conflict was Makron, one of the most influential red-figure painters in early fifth-century-B.C. Athens. He was exceptionally prolific, with more than six hundred extant vases attributed to him, and he appears to have worked exclusively with one potter, Hieron.
Catalogue Raisonné
Caskey-Beazley, Attic Vase Paintings (MFA), no. 140; Highlights: Classical Art (MFA), p. 061.
DescriptionSide A: Paris (named Alexandros here) is leading Helen away from Sparta and the Palace of Menelaos. Aeneas, with a lion shield, accompanies Paris. Aphrodite and Eros flank Helen. Peitho, the personification of persuasion, follows behind Aphrodite. The boy under the handle is thought to be Helen's son by Menelaos.
Side B: During the sack of Troy. Helen fleeing to the Sanctuary of Apollo. Menelaos, at the right, sees Helen and draws his sword to kill her. Aphrodite is behind Helen, present as an intervening force. Menelaos is in the act of dropping his sword, overcome by Helen's beauty. The priest of the sanctuary, Chryses, and his daughter, Chryseis are also present (at far left). Priam is seated under handle at the right, watching the story unfold.
Painted inscriptions: "Aineas"; "Alexandros"; "Aphrodite" (twice); "Priam"; "Helen" (twice); "Kriseis"; "Kriseus"; "Menelaos"
Scratched on handle: "Hieron made (it)" (HIERON EPOIESEN)
Painted under the opposite handle: "Makron drew (it)" (MAKRON EGRAPHSEN)
The size of this vessel suggests it was made for display, rather than use, and like huge kylikes (parade cups) of the same period which could not have been used for drinking.
Side B: During the sack of Troy. Helen fleeing to the Sanctuary of Apollo. Menelaos, at the right, sees Helen and draws his sword to kill her. Aphrodite is behind Helen, present as an intervening force. Menelaos is in the act of dropping his sword, overcome by Helen's beauty. The priest of the sanctuary, Chryses, and his daughter, Chryseis are also present (at far left). Priam is seated under handle at the right, watching the story unfold.
Painted inscriptions: "Aineas"; "Alexandros"; "Aphrodite" (twice); "Priam"; "Helen" (twice); "Kriseis"; "Kriseus"; "Menelaos"
Scratched on handle: "Hieron made (it)" (HIERON EPOIESEN)
Painted under the opposite handle: "Makron drew (it)" (MAKRON EGRAPHSEN)
The size of this vessel suggests it was made for display, rather than use, and like huge kylikes (parade cups) of the same period which could not have been used for drinking.
Signed
Scratched on handle: "Hieron made (it)" (HIERON EPOIESEN)
Painted under the opposite handle: "Makron drew (it)" (MAKRON EGRAPHSEN)
Painted under the opposite handle: "Makron drew (it)" (MAKRON EGRAPHSEN)
InscriptionsInscriptions: "Aineas"; "Alexandros"; "Aphrodite" (twice); "Priam"; "Helen" (twice); "Kriseis"; "Kriseus"; "Menelaos", "Hieron "made [it] (HIERON EPOIESEN), "Makron painted [it]" (MAKRON EGRAPHSEN)
ProvenanceMay 22, 1879, found next to a tomb at the necropolis of Suessula by Marchese Marcello Spinelli, Cancello, Italy [see note 1]; sold by Spinelli to Edward Perry Warren (b. 1860 - d. 1928), London and Rome; 1913, sold by Warren to the MFA for $18,948.70 [see note 2]. (Accession Date: January 2, 1913)
NOTES:
[1] F. von Duhn, "Scavi nella necropoli di Suessula," Bullettino dell'Instituto di corrispondenza archeologica 1879, p. 150. [2] Total purchase price for MFA accession nos. 13.186-13.245.
NOTES:
[1] F. von Duhn, "Scavi nella necropoli di Suessula," Bullettino dell'Instituto di corrispondenza archeologica 1879, p. 150. [2] Total purchase price for MFA accession nos. 13.186-13.245.